Human colonisation is not to be confused with colonialism or imperialism, as colonisation is a broader category, encompassing all large-scale immigrations of an established population to a 'new' location, and expansion of their civilisation into this area. This process may or may not victimise the native population (depending first on whether there is any indigenous population to victimise).
Colonialism is the extension of a nation's sovereignty over territory
beyond its borders by the establishment of either settler colonies or
administrative dependencies in which indigenous populations are directly ruled
or displaced. Colonizers generally dominate the resources, labor, and markets of
the colonial territory and may also impose socio-cultural, religious and
linguistic structures on the conquered population; this has led critics of
colonialism to call it cultural imperialism.
The historical phenomenon of European colonisation may be broadly divided into two large waves, the first one starting with the 'Age of Exploration' and the beginning of the 'Columbian Exchange' after 1492; and the second one beginning in the second part of the 19th century with the New Imperialism period.
Two different models of colonization:
1. The British Empire created the Commonwealth and used indirect rule, allowing the local elites to govern the colonies, under the supervision of the colonial administration.
2. the French Third Republic (1871-1940) directly ruled
over the colonies, claiming they were integrally part of the French Republic.
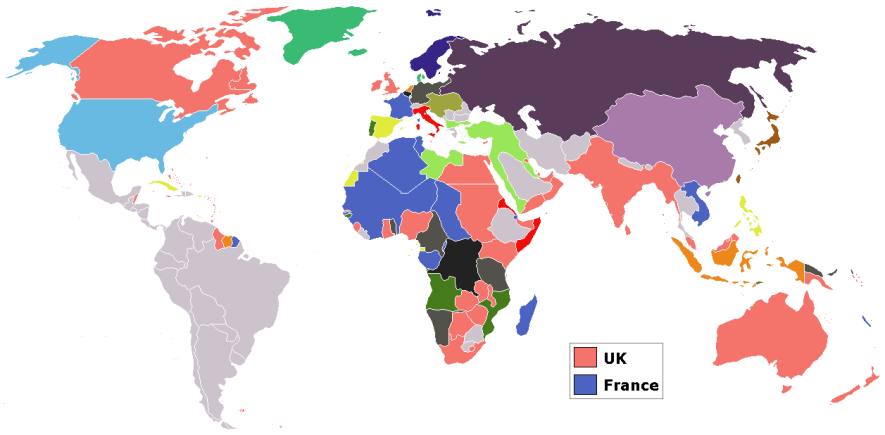
World in 1898, showing the largest colonial empires.

credits:
The text was extracted from Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia under GNU Free Documentation Licence.