Welsh Assembly Building in Cardif bay

The debating chamber in the Welsh Parliament (Senedd)

An overview of the National Assembly for Wales
|
Welsh Assembly Building in Cardif bay
|
The debating chamber in the Welsh Parliament (Senedd)
|
The new Assembly building (the transparent building next to the red brick Pier Head) in Cardiff Bay was officially opened by Her Majesty The Queen on St. David's Day (the patron saint of Wales) March 1st, 2006.
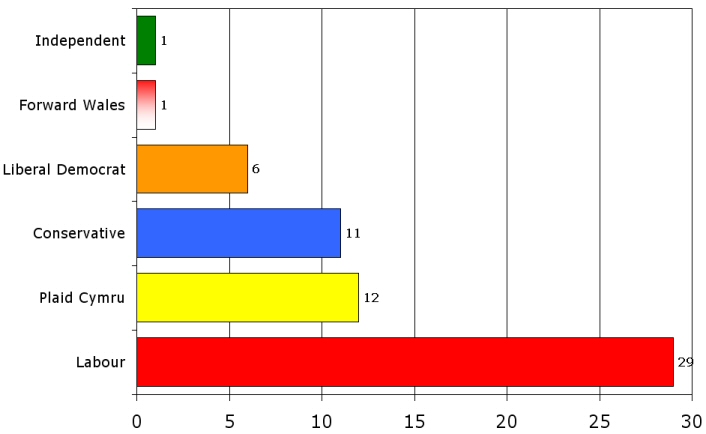
In a referendum in May 1997, the Welsh people narrowly approved (50.3% voted in favour and 49.7% against it) government proposals (promised by Tony Blair in his election campaign in 1997) to devolve certain powers and responsibilities to a Welsh National Assembly. The National Assembly for Wales held its first elections in May 1999 and began functioning as a devolved administration in July 1999. Same as in Hungary, people cast two votes in Assembly elections: one for a candidate in their local constituency and one for a party list. The Assembly comprises 60 members (called AMs instead of MPs; in Welsh: AC - Aelod y Cynulliad): 40 from local constituencies. The Labour Party has historically had strong support in Wales. It has the largest number of seats in the Assembly, although it does not have an overall majority. Since October 2000 the Labour Party has run the Assembly in partnership with the Liberal Democrats. The Official Opposition party (the second largest party) in the National Assembly is Plaid Cymru (The Party of Wales).
Composition of the present Assembly, seats by parties
Responsibilities
The National Assembly for Wales has powers to make secondary legislation to meet distinctive Welsh needs. The current legislative powers of the Welsh Assembly are more limited than the Scottish Parliament or the Northern Ireland Assembly in the UK or state legislatures in the United States. The Welsh Assembly is responsible for:
§ economic development
§ agriculture, forestry, fisheries and food
§ education and training (e.g.
Charges for University Tuition)§ industry
§ local government
§ health and personal social services (e.g. Setting the prices for NHS prescreptions in Wales - considerably less than in England!)
§ housing
§ environment planning
§ transport and roads
§ arts, culture and the Welsh language
§ ancient monuments and historic buildings
§ sport and recreation
In January 2000 the Assembly Cabinet published Better Wales - its ten-year strategy built round five key areas for improving life in Wales: opportunities for learning; a stronger economy; better health and quality of life; and better, simpler government. Better Wales also set out more than 100 targets for achievement by the end of the current Assembly including: no infant classes with more than 30 pupils; a 10% increase in the number of Welsh exporting companies; and the number of tourism trips to increase to 12.2 million per year. In October 2000 the First Minister, who heads the Assembly, appointed a Cabinet of eight ministers in charge of: economic development; finance and communities; education and lifelong learning; health and social services; culture and sports; rural affairs; environment; and business. The Assembly is also responsible for over 50 public bodies. The organisations with the largest expenditure are: the Higher Education Funding Council for Wales; and the Welsh Development Agency (WDA).
Role of the UK Government in Wales
Following devolution, the UK Government has kept responsibility in Wales for certain matters including:
§ foreign affairs
§ defence
§ taxation
§ overall economic policy
§ crime, justice and prisons
§ social security
§ broadcasting
The office of Secretary of State for Wales continues. The post holder has a seat in the UK Cabinet and is responsible for promoting the devolution settlement, bringing forward primary legislation, bidding for the Assembly’s budget and ensuring that Welsh interests are properly represented and considered within the UK Government. As part of the UK, Wales retains full constituency representation in the Westminster Parliament.
learn more:
National Assembly for Wales Official Site
sources:
National Statistics, UK 2002, The Official Yearbook of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
National Assembly for Wales Official Site
Wikipedia, National Assembly for Wales
credits:
The text was composed by using the relevant materials of...
1. The Official Yearbook of GB and NI © Crown Copyright 2001, under PSI licence
2. Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia under GNU Free Documentation Licence.